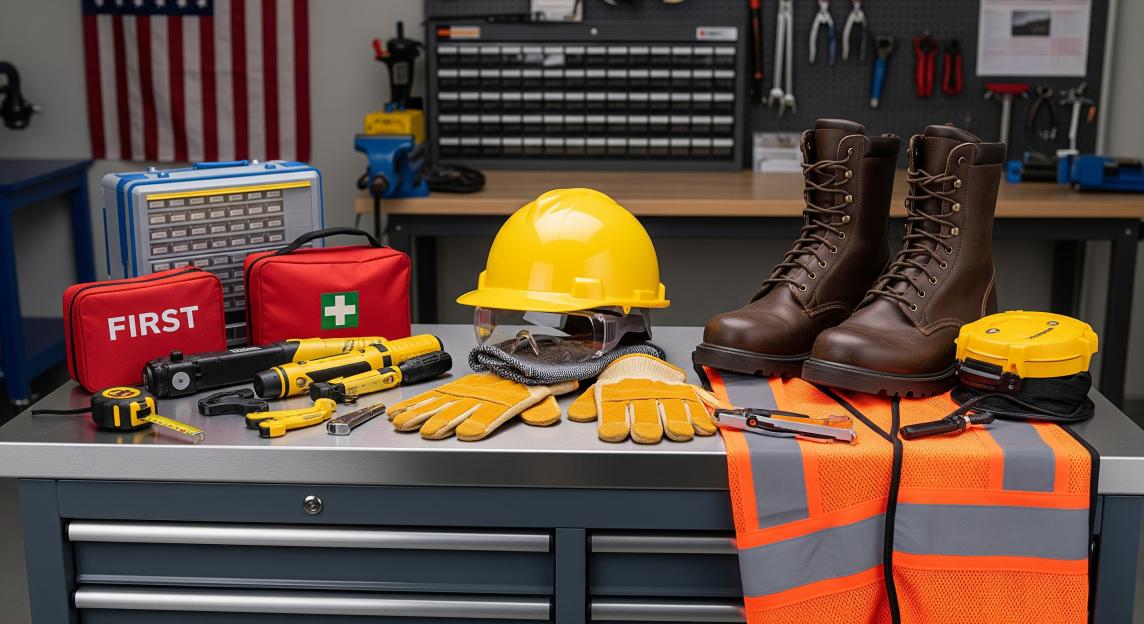
The screech of metal against concrete. The sudden crack of wood under pressure. The split-second when you realize danger is just inches away from your fingertips. In those heart-stopping moments, the difference between a close call and a tragedy often comes down to one thing: having the right safety tools within reach.
Every year, thousands of Americans face preventable accidents that could have been avoided with proper safety equipment. Whether you’re a weekend warrior tackling home improvement projects, a professional tradesperson, or simply a parent wanting to protect your family, understanding and investing in quality safety tools isn’t just smart-it’s essential for preserving what matters most.
Understanding Safety Tools: Your First Line of Defense
Safety tools encompass a broad range of equipment designed to protect people from harm in various environments. These protective devices serve as barriers between you and potential hazards, whether you’re working with power tools in your garage, handling chemicals in a laboratory, or simply preparing for emergencies at home.
The importance of safety equipment cannot be overstated. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and safety tools prevents millions of workplace injuries annually. Beyond professional settings, home safety tools play a crucial role in protecting families from everyday hazards.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Your Essential Armor
Eye Protection: Safeguarding Your Vision
Your eyes are irreplaceable, making eye protection one of the most critical safety investments you can make. Safety glasses and goggles protect against flying debris, chemical splashes, and harmful radiation.
Safety Glasses vs. Safety Goggles:
- Safety glasses offer basic protection for light-duty tasks
- Safety goggles provide comprehensive coverage for high-risk activities
- Prescription safety glasses combine vision correction with protection
- Side shields enhance peripheral protection
When selecting eye protection, look for ANSI Z87.1 certification, which ensures the eyewear meets rigorous safety standards. Popular brands like 3M, Honeywell, and Uvex offer reliable options for various applications.
Head Protection: Hard Hats and Safety Helmets
Construction sites, industrial facilities, and even some home projects require head protection. Modern hard hats protect against falling objects, electrical hazards, and impact injuries.
Types of Head Protection:
- Type I hard hats protect against top impacts
- Type II hard hats offer lateral and top protection
- Climbing helmets for recreational and professional use
- Bump caps for low-clearance areas
Key features to consider include suspension systems, ventilation, accessory slots for lights or ear protection, and electrical insulation ratings.
Hand Protection: Gloves for Every Task
Your hands are your most valuable tools, making proper glove selection crucial for safety and productivity. Different tasks require specific glove types:
Work Gloves by Material:
- Leather gloves for general construction and handling
- Nitrile gloves for chemical resistance
- Cut-resistant gloves for sharp object handling
- Insulated gloves for electrical work
- Disposable gloves for hygiene and contamination prevention
Consider factors like grip, dexterity, durability, and specific hazard protection when choosing work gloves.
Foot Protection: Safety Boots and Shoes
Proper footwear protects against punctures, crushing injuries, electrical hazards, and slips. Safety footwear features vary based on workplace requirements.
Safety Footwear Features:
- Steel toes for impact protection
- Composite toes for lighter weight
- Puncture-resistant soles
- Electrical hazard protection
- Slip-resistant outsoles
- Waterproof construction
Brands like Red Wing, Timberland PRO, and Caterpillar offer comprehensive safety footwear lines for various industries.
Respiratory Protection: Breathing Safely
Clean air is fundamental to health, making respiratory protection essential in many environments. From dust masks to full-face respirators, proper breathing protection prevents lung damage and illness.
Respiratory Protection Types:
- N95 masks for particulate filtration
- P100 respirators for higher protection levels
- Half-face respirators with replaceable cartridges
- Full-face respirators for maximum protection
- Powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs)
Proper fit testing ensures respiratory protection works effectively. Different cartridges protect against specific contaminants like organic vapors, acids, or ammonia.
Fall Protection Equipment: Working at Heights Safely
Falls remain a leading cause of workplace fatalities, making fall protection systems critical for elevated work. Modern fall protection equipment provides multiple safety layers.
Harnesses and Safety Belts
Full-body harnesses distribute fall forces across the body, reducing injury risk. Key harness features include:
- Adjustable leg and chest straps
- Multiple attachment points
- Quick-connect buckles
- Padding for comfort during extended wear
- Tool attachment loops
Lanyards and Lifelines
Lanyards connect harnesses to anchor points, while lifelines provide continuous protection along work paths. Options include:
- Shock-absorbing lanyards to reduce fall forces
- Retractable lifelines for freedom of movement
- Horizontal lifelines for multiple workers
- Vertical lifelines for climbing applications
Anchors and Tie-Off Points
Secure anchor points are essential for effective fall protection. Temporary and permanent anchor options include:
- Roof anchors for construction work
- I-beam clamps for steel structures
- Concrete anchors for permanent installations
- Mobile anchor carts for flexibility
First Aid and Emergency Equipment: Preparing for the Unexpected
Even with preventive measures, accidents happen. Comprehensive first aid supplies and emergency equipment enable quick response to injuries and emergencies.
First Aid Kits: Essential Medical Supplies
Well-stocked first aid kits should contain supplies for treating common injuries:
- Adhesive bandages in various sizes
- Sterile gauze pads and medical tape
- Antiseptic wipes and ointments
- Instant cold packs
- Elastic bandages
- Scissors and tweezers
- Disposable gloves
- Emergency medications
OSHA provides specific first aid kit requirements based on workplace size and hazard levels.
Emergency Communication Tools
Reliable communication during emergencies can save lives. Essential communication tools include:
- Two-way radios for team coordination
- Emergency whistles for signaling distress
- Cell phone signal boosters
- Satellite communicators for remote areas
- Emergency beacons for outdoor activities
Fire Safety Equipment
Fire extinguishers, smoke detectors, and fire blankets provide crucial fire protection:
- Class A extinguishers for ordinary combustibles
- Class B extinguishers for flammable liquids
- Class C extinguishers for electrical fires
- Class K extinguishers for cooking fires
- Multi-purpose ABC extinguishers for versatility
Regular maintenance and inspection ensure fire safety equipment functions when needed.
Safety Tools for Specific Industries
Construction Safety Equipment
Construction sites present numerous hazards requiring specialized safety tools:
- Traffic control devices for roadwork safety
- Confined space entry equipment
- Scaffolding safety systems
- Crane and rigging hardware
- Excavation protection systems
Manufacturing Safety Tools
Manufacturing environments require specific safety solutions:
- Machine guarding systems
- Lockout/tagout (LOTO) devices
- Ergonomic lifting aids
- Anti-fatigue mats
- Safety shower and eyewash stations
Laboratory Safety Equipment
Research and testing facilities need specialized safety tools:
- Chemical fume hoods
- Safety cabinets for chemical storage
- Spill containment systems
- Emergency deluge showers
- Chemical-resistant lab equipment
Home Safety Tools: Protecting Your Family
Home safety extends beyond professional environments. Essential home safety tools include:
Basic Home Safety Equipment
- Smoke and carbon monoxide detectors
- Fire extinguishers appropriate for home use
- First aid kits stocked for family needs
- Emergency flashlights and batteries
- Non-slip mats for bathrooms and stairs
Workshop and Garage Safety
Home workshops require professional-grade safety equipment:
- Dust collection systems
- Adequate lighting
- Proper ventilation
- Tool guards and safety devices
- Appropriate storage for hazardous materials
Child Safety Tools
Protecting children requires specialized safety equipment:
- Outlet covers and plug protectors
- Cabinet and drawer locks
- Stair gates and window guards
- Pool safety equipment
- Car seats and booster seats
Technology and Innovation in Safety Tools
Modern safety tools incorporate advanced technology for enhanced protection:
Smart Safety Equipment
Connected safety devices provide real-time monitoring:
- Smart hard hats with impact sensors
- GPS-enabled safety devices for lone workers
- Air quality monitors with smartphone alerts
- Wearable devices tracking worker fatigue
Advanced Materials
New materials improve safety tool performance:
- Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene for cut resistance
- Advanced composites for lighter protective equipment
- Moisture-wicking fabrics for improved comfort
- Anti-microbial treatments for hygiene
IoT Integration
Internet of Things (IoT) technology enables comprehensive safety monitoring:
- Connected gas detectors
- Automated emergency response systems
- Predictive maintenance for safety equipment
- Real-time safety compliance monitoring
Choosing the Right Safety Tools: A Buyer’s Guide
Assessing Your Safety Needs
Proper safety tool selection begins with hazard assessment:
- Identify potential risks in your environment
- Evaluate the severity and likelihood of hazards
- Determine appropriate protection levels
- Consider regulatory requirements
- Budget for quality equipment
Quality Standards and Certifications
Look for recognized safety certifications:
- ANSI (American National Standards Institute)
- OSHA compliance markings
- NIOSH approval for respiratory protection
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories) listings
- CSA (Canadian Standards Association) marks
Brand Recommendations and Reviews
Research reputable safety equipment manufacturers:
- 3M for comprehensive safety solutions
- Honeywell for industrial safety equipment
- MSA Safety for gas detection and fall protection
- DuPont for chemical protective clothing
- Klein Tools for electrician safety equipment
Read user reviews and professional evaluations to make informed decisions.
Maintenance and Care of Safety Equipment
Regular Inspection Procedures
Establish routine inspection schedules:
- Daily visual inspections before use
- Weekly detailed examinations
- Monthly comprehensive assessments
- Annual professional inspections
- Post-incident evaluations
Cleaning and Storage Best Practices
Proper maintenance extends equipment life:
- Clean equipment according to manufacturer instructions
- Store in designated areas away from contaminants
- Protect from extreme temperatures and UV exposure
- Maintain inventory records and expiration dates
- Replace damaged or expired equipment promptly
Replacement Schedules
Establish replacement timelines:
- Hard hats: every 2-5 years depending on use
- Safety glasses: when scratched or damaged
- Respirator cartridges: according to manufacturer guidelines
- Fall protection equipment: per inspection results
- First aid supplies: before expiration dates
Training and Education: Using Safety Tools Effectively
Proper Usage Training
Equipment effectiveness depends on proper use:
- Manufacturer training programs
- OSHA-required safety training
- Hands-on practice sessions
- Regular refresher courses
- Peer-to-peer knowledge sharing
Safety Culture Development
Building a safety-first mindset:
- Leadership commitment to safety
- Employee involvement in safety programs
- Recognition of safe practices
- Open communication about safety concerns
- Continuous improvement initiatives
Staying Updated on Safety Regulations
Keep current with safety requirements:
- Subscribe to OSHA updates
- Attend industry safety conferences
- Join professional safety organizations
- Monitor regulatory changes
- Participate in safety committees
Cost Considerations and ROI of Safety Tools
Initial Investment vs. Long-term Savings
Quality safety equipment provides significant returns:
- Reduced medical costs from prevented injuries
- Lower insurance premiums
- Decreased workers’ compensation claims
- Improved productivity from confident workers
- Avoided regulatory fines and penalties
Budget-Friendly Safety Solutions
Maximize safety on limited budgets:
- Prioritize high-risk hazards first
- Consider multi-purpose equipment
- Buy quality items that last longer
- Take advantage of bulk purchasing discounts
- Implement preventive maintenance programs
Government Incentives and Programs
Explore available assistance:
- OSHA consultation programs
- State safety grants
- Insurance company safety rebates
- Tax deductions for safety equipment
- Training assistance programs
Building a Comprehensive Safety Program
Risk Assessment and Planning
Develop systematic safety approaches:
- Conduct thorough hazard assessments
- Prioritize risks by severity and probability
- Select appropriate safety tools and equipment
- Develop safety procedures and protocols
- Implement training and education programs
Implementation Strategies
Successfully deploy safety programs:
- Start with leadership commitment
- Involve employees in planning
- Provide adequate resources
- Establish clear expectations
- Monitor and measure progress
Continuous Improvement
Maintain effective safety programs:
- Regular program evaluations
- Employee feedback collection
- Incident investigation and analysis
- Best practice sharing
- Technology adoption
Emergency Preparedness: Beyond Basic Safety Tools
Disaster Planning
Prepare for natural and man-made emergencies:
- Emergency action plans
- Evacuation procedures
- Communication systems
- Backup power sources
- Emergency supply stockpiles
Recovery Equipment
Tools for post-emergency situations:
- Damage assessment equipment
- Temporary protection materials
- Cleanup and restoration tools
- Documentation supplies
- Communication devices
Community Safety Resources
Connect with local safety resources:
- Emergency management agencies
- Fire departments and EMS
- Local hospitals and medical facilities
- Mutual aid agreements
- Emergency shelters and services
Future Trends in Safety Technology
Emerging Technologies
New developments in safety equipment:
- Artificial intelligence for hazard prediction
- Augmented reality for safety training
- Nanotechnology for improved materials
- Robotics for dangerous task automation
- Biometric monitoring for health tracking
Sustainability in Safety Equipment
Environmental considerations:
- Recyclable materials in safety equipment
- Reduced packaging and waste
- Energy-efficient safety systems
- Sustainable manufacturing processes
- End-of-life equipment disposal programs
Global Safety Standards
International harmonization efforts:
- ISO safety standards adoption
- Global supply chain safety requirements
- Cross-border safety compliance
- International best practice sharing
- Multinational safety training programs
Conclusion: Your Safety Investment Pays Dividends
Investing in quality safety tools isn’t just about compliance or avoiding accidents-it’s about creating an environment where people can work confidently, families can thrive, and communities can prosper. The right safety equipment serves as your invisible guardian, standing ready to protect when seconds matter most.
From the basic hard hat protecting a construction worker to the sophisticated gas detection system safeguarding an entire facility, safety tools represent humanity’s commitment to protecting what matters most: each other. As technology advances and our understanding of safety deepens, these tools will continue evolving, but their fundamental purpose remains unchanged-keeping people safe so they can return home healthy to their loved ones every day.
Remember, the best safety tool is the one you have with you when you need it. Make safety a priority, invest in quality equipment, maintain it properly, and never compromise when it comes to protection. Your future self-and your family-will thank you for making safety a non-negotiable part of your daily routine.
The choice is yours: will you be prepared when danger strikes, or will you wish you had been? Choose preparation. Choose protection. Choose safety tools that work as hard as you do to keep everyone safe.